CMDB (Central Repository for Configuration Management
- Elements comprising the CMDB
- Data sources contained in the CMDB
- ITSM process support
Table of contents
CMDB
Configuration Management Database is a repository that stores information about IT infrastructure components. It allows you to view, modify and provision all system resources, known as configuration items (CI). It contains a list of items (CI), their attributes and shows the interrelationships between them. ts purpose is to improve operational decision-making and control the status of IT resources. The CMDB records the following types of data regarding, among other things:
- computer hardware,
- software,
- networks,
- locations,
- documentation,
- license.
This functionality in the eAuditor system makes it possible to obtain and store information about IT infrastructure components within a single software. Collections, databases and configuration units are updated in real time. As a result, network administrators have up-to-date information and can manage configuration items from more than 25 categories. All resources shared in the CMDB repository are grouped by domain. The range of groups is constantly being expanded. Due to the complexity of the system, it is possible to collect data from multiple sources. CMDB resources are grouped by domain. he scope of groups depends on the version of the eAuditor system and is constantly being developed.
CMDB is also configured in the console with LDAP servers from which user data is imported and updated. This allows you to enter any number of servers for different domains. In addition, the view available within the CMDB allows defining and sending eLearning messages. These are used to send users the training implemented into the system, according to a defined schedule. As a result, the administrator only needs to set up the messages once according to a dedicated schedule and will not have to remember this action again. . This reduces the work time that an administrator would have to spend on sending messages to each employee individually.
In addition, there is also a list of definable locations to which the administrator can assign individual users. Unlike the organizational structure, the data is not imported from Active Directory. In addition, the eAuditor system within the CMDB also monitors network services divided by their corresponding categories. The situation is similar with regard to network ports, which are also monitored along with the service and the category to which the service belongs.
Benefits of using a CMDB
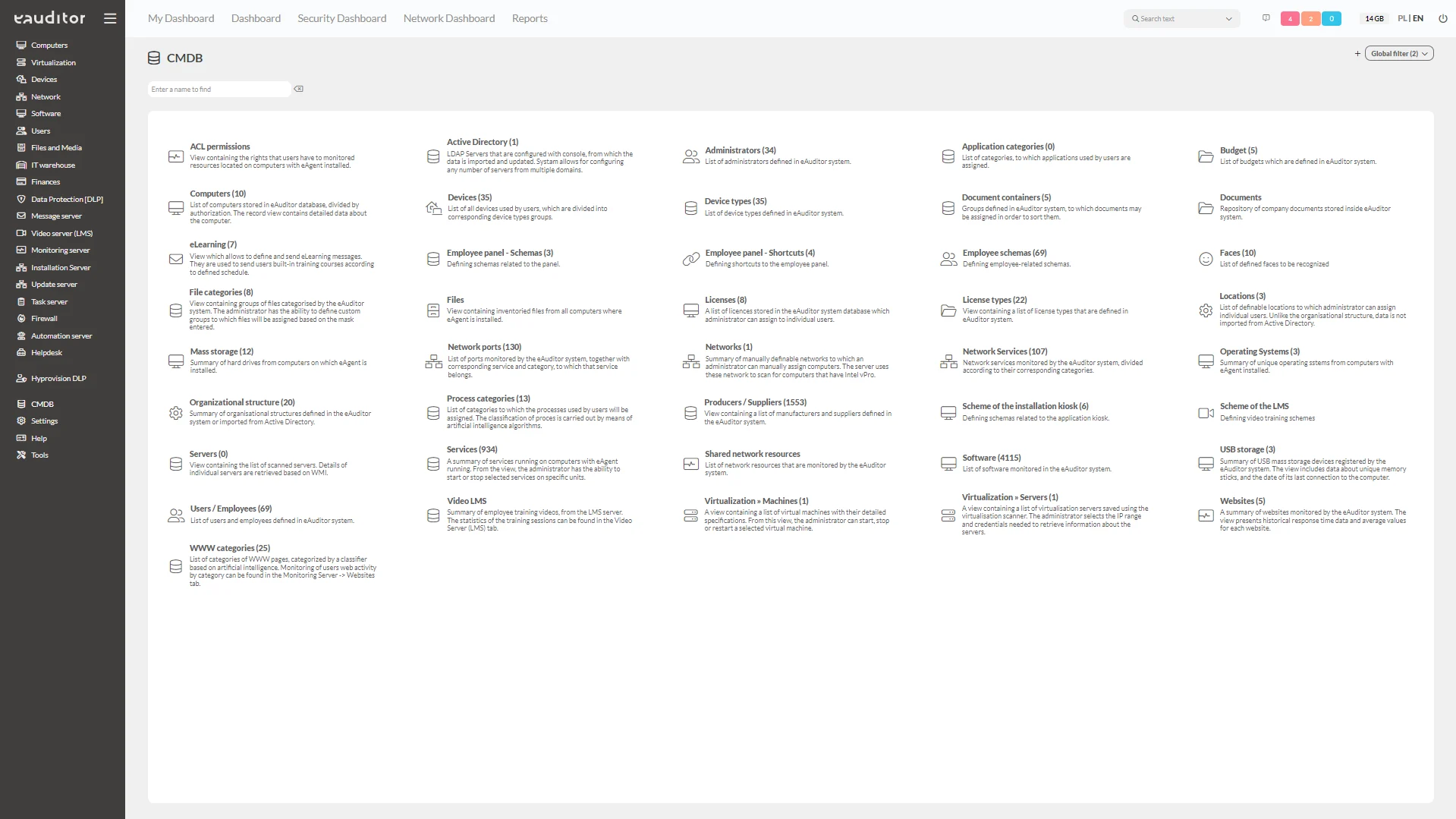
Elements included in the CMDB
Within the CMDB, the administrator has access to the following elements.
Sources of data contained in the CMDB
All the data contained in the CMDB comes from:
- network scanner,
- virtualization scanner,
- Microsoft Active Directory (MS AD),
- BTC AI cloud computing repositories,
- integrated systems (eHelpdesk, Hyprovision DLP, RODOprotector, others),
- external files,
- API interjes data,
- manual record-keeping processes.